Clot in a Neck Artery
The main arteries in the neck are the carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries. A blood clot in a neck artery might cause a stroke. There is more than one cause for a clot to form in one of the neck arteries. Many people with these clots will actually not have any symptoms. And when symptoms do happen, stroke is only one options.
What Causes a Clot in a Neck Artery?
Like in other cases of artery blood clots, there can be more than one cause. This is important, because the causes, and treatments are very different.
One option is plaque buildup over the years. Plaque is a combination of fat, calcium and cells. It is a manifestation of atherosclerosis. Poor lifestyle together with genetic causes come together to cause plaque. Plaque slowly builds up over time and causes growing degrees of narrowing of the artery. But sometimes a plaque might rupture. A ruptured plaque will trigger clots that can migrate into the brain and cause a stroke.
Another cause for a clot in a neck artery is an injury. Of course, a severe injury might tear an artery altogether. But a more common type of injury is called an artery dissection. A dissection is when the layers of the artery separate. If this happens, the inner layers of the artery are exposed. The body reacts to a dissection by forming blood clots at the location of the injury. But sometimes the clots might grow and block the artery. Other times, pieces of the clot might migrate into the brain. Of course, this can cause a stroke.
Symptoms
Not everyone with a carotid artery clot will have symptoms. In fact, many people will not have symptoms. First, we cannot really sense slow buildup of plaque. But even if there is a clot that suddenly blocks the artery, a person might be lucky and stay without symptoms. This is because many people have enough extra blood flow to compensate for the blocked artery.
But sometimes there are symptoms. First, there might be stroke symptoms. The most common stroke symptoms are weakness of a limb, drooping of the mouth edge and an inability to speak or understand. If the clot blocks the artery to the eye, there could be blindness in one eye. This is also called amaurosis fugax. But remember that a stroke might cause many other neurological symptoms. And not all of these symptoms are easy to diagnose.
Other symptoms are also possible. Some people who develop a carotid artery dissection will experience neck pain. Also, headache is a typical symptom. Obviously, many people suffer from neck pain. So it might be hard to tell the difference. But neck pain or a headache that start suddenly might signify a neurological emergency.
Diagnosis of a Clot in a Neck Artery
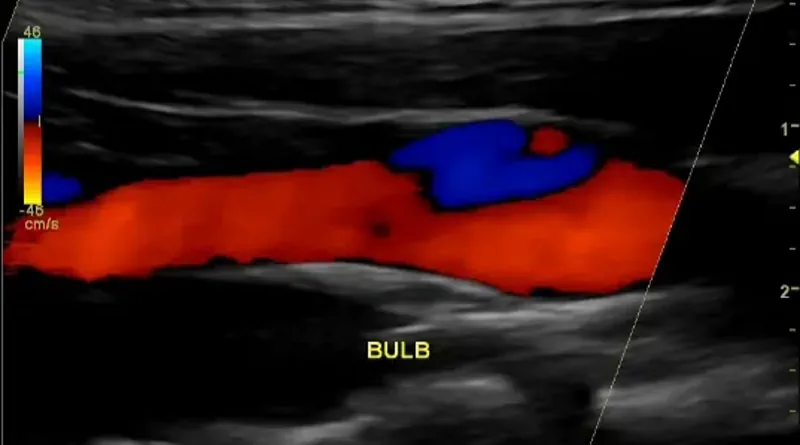
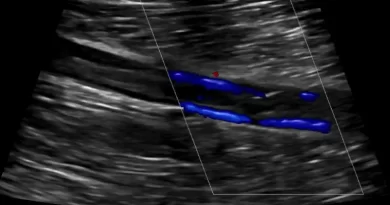
You cannot diagnose a clot in a neck artery without imaging. Imaging means taking pictures of the artery to see if there is a clot. The easiest test is an ultrasound. A carotid artery ultrasound will be able to show blockages in the neck arteries.
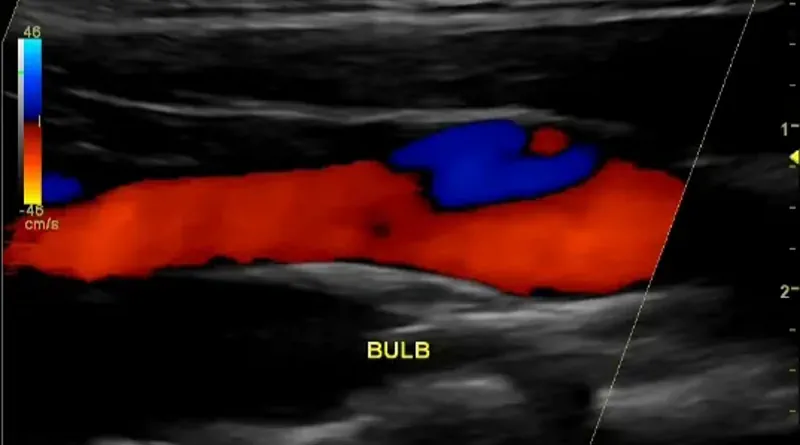
Sometimes ultrasound can even show a dissection, but it is not the best test for this purpose. If you need more accurate pictures, you will choose a CT scan or an MRI. In most places it is easier to get a high quality CT scan. A CT scan of the neck arteries will show blockages and any other problems that might exist there. It is very accurate.
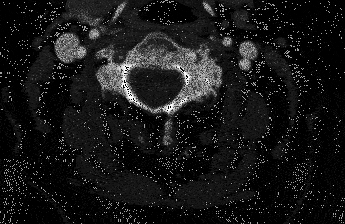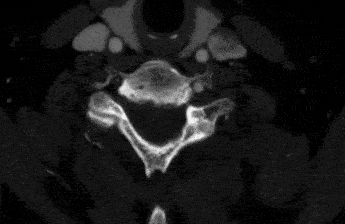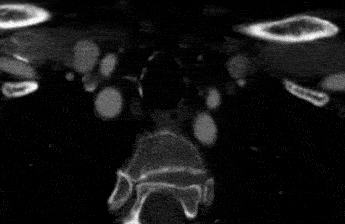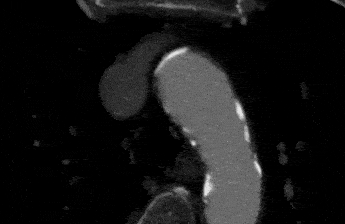
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the exact problem. Also, treatment includes medication and procedures.
Medication
Medication to treat a clot in a neck artery is with blood thinners. Usually the type of blood thinner will be aspirin. But we will give some people who are having a stroke, clot busting medication called thrombolytics.
To prevent blockages from growing or from rupturing, we will give medications called statins. Statins treat high cholesterol levels. But they also stabilize plaque and prevent it from rupturing.
Procedures
Most people will not need a procedure, even if they have a significant clot. But procedures do exist. There are procedures to suck clot out of the neck arteries or brain arteries. There are other procedures to open blockages in the neck arteries. Opening these blockages can be with surgery or with balloons and stents.


Pingback: Clot in a Heart Artery: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment