Blood Clots in Legs
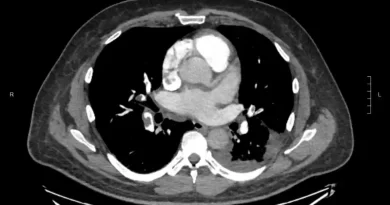
Sudden calf swelling and pain may be the signs of blood clots in leg veins. Blood clots in legs are also called deep vein thrombosis or DVT. These clots can cause local problems in the legs or move to the lungs where they become pulmonary embolism, PE.
What Causes Blood Clots in Legs?
Most people who have a blood clot worry about cancer. And yes, it is true that cancer is a cause of clotting. But there are many other causes for blood clots in legs.
Broadly, we divide clots into:
- Provoked
- Unprovoked
Provoked clots have a clear reason. For instance blood clots after surgery are a classic example. On the other hand, unprovoked clots are more complicated. Obviously they happened for a reason. But that reason is not as straightforward as surgery or an injury.
And then there are clots that are hard to define. For instance, blood clots after flying. Many people fly and most never have a clot. So while technically flying does increase the risk for clotting, why does it affect some people more than others?
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Legs
When it forms, a clot in a leg vein will cause pain and swelling in that leg. Calf swelling is probably the most common symptom.
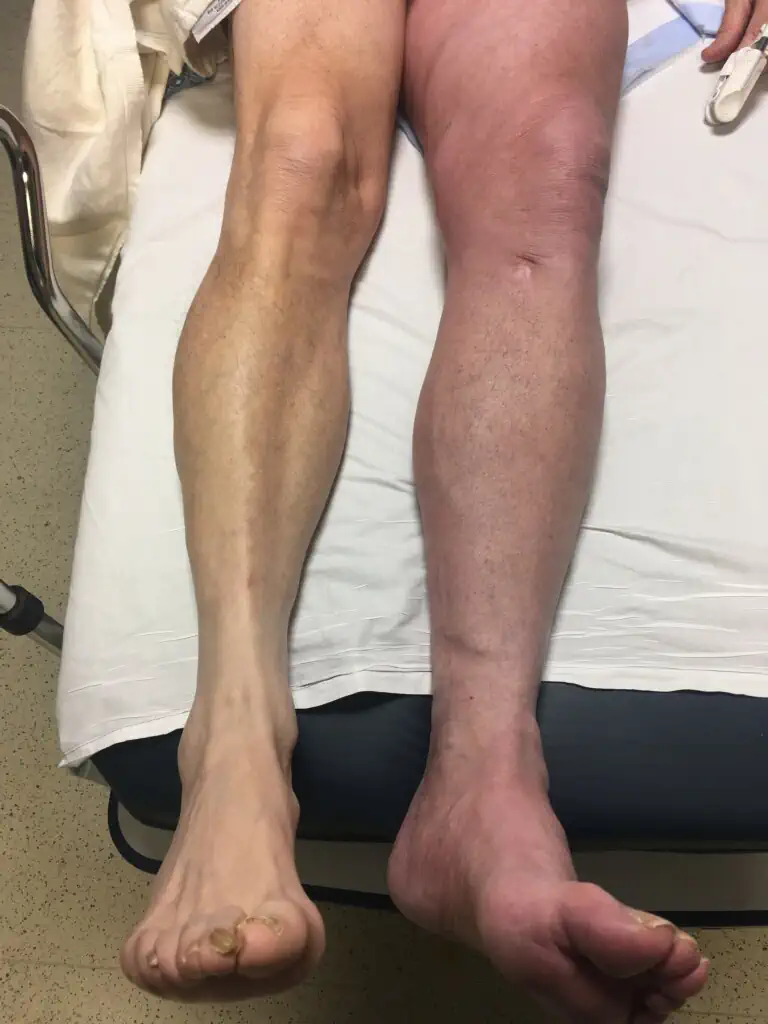
But many people with these clots will not have any symptoms at all. Sometimes, the clots are found when a scan is performed for another reason.
Phlegmasia
Sometimes, a blood clot in a vein will cause so much swelling and pressure in the leg, that it will block off the blood flow in the arteries. When that happens we call it phlegmasia. Phlegmasia is a medical emergency. Unless the clot is removed quickly from the vein, a person might lose a leg or even die as a result of this complication.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
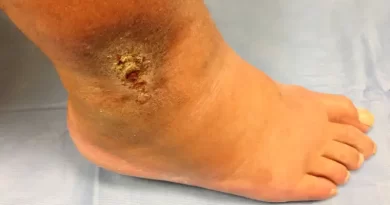
With time, the symptoms will change. In some people the symptoms will resolve completely. But in others, long-term symptoms will develop. These are called post-thrombotic syndrome. Another name is post-phlebitic syndrome. The symptoms of post-thrombotic syndrome are variable. In some people there is just some leftover ankle swelling. But other people will develop more severe symptoms. For instance, chronic severe leg swelling, pain, and aches. Sometimes, people will even develop chronic skin changes and even venous wounds.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots in Legs
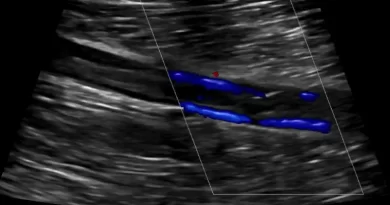
The main tool to make the diagnosis of a deep vein thrombosis is an ultrasound. Ultrasound uses sound waves to visualize the blood flow in the veins. An ultrasound is accurate in proving the presence of blood clots in leg veins.
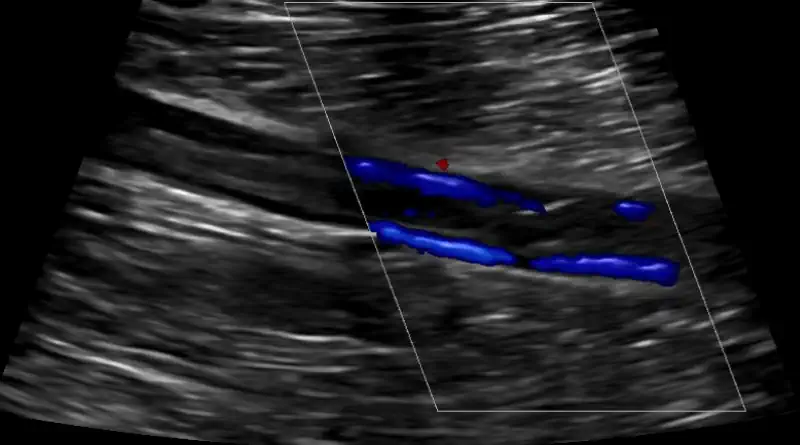
In theory, there are other tools to make the diagnosis. For instance, both CT and MRI can show vein blood clots.
Treatment
The best treatment for any vein blood clot are blood thinners. Blood clots in legs are not different. It is important to start the blood thinners as soon as possible after the diagnosis.
Procedures to Treat Blood Clots in Legs
There are two purposes for a procedure in the treatment of blood clots in legs. First, to help with severe symptoms. And second, to prevent long-term problems like the post-thrombotic syndrome.
But here’s the problem. We know that procedures work to help with the acute symptoms. On the other hand, it is very hard to know who to offer a procedure to prevent long-term issues. There have been severe scientific studies that looked into this question. The most famous of these is called the ATTRACT trial. Another large study is called the CAVA trial. Unfortunately, while there probably are people who will benefit from a procedure, most will not.
How Long do I need to Take the Blood Thinner for?
Most people will need to take a blood thinner for at least three months after a blood clot in a leg vein. But some people will need to continue to take them for a longer period.
Here are some factors we consider when we try to decide how long to treat for:
- What caused the clot? Was it provoked or unprovoked?
- Can we eliminate whatever the cause was? For instance, you stop taking oral contraceptive pills. But some things you cannot change. Like metastatic cancer.
- What is your risk for bleeding? If the risk is high, we will favor a shorter time on a blood thinner
- How bad was the clot? We sometimes decide to treat for a longer period if the original event was worse
- Are you back to normal? Because if you still have symptoms related to your clot, maybe you need to stay on the blood thinners